Decarbonisation and transitioning between traditional energy sources is no small task. Baker Hughes weighs in on how AI and new technologies are enabling efficiency and efficacy.
Nothing’s Vision for the Future of AI Smartphones: A Direct Interview with CEO Carl Pei
Understand how Nothing leverages cutting-edge technologies instead of large language models to improve smartphone AI experiences.
Google Cloud Launches Gemini Enterprise, an All-in-One Agentic AI Platform for the Workplace
Gemini Enterprise is Google Cloud’s latest innovation, providing a unified interface for advanced AI in the workplace to enhance efficiency.
Amazon Launches Redesigned Kindle Scribes with Colour and AI
Amazon announces a new line of Kindle Scribe e-readers including the Kindle Scribe Colorsoft which brings colours and a large 11-inch screen.
Open AI to Deploy up to 6GW of AMD Instinct GPUs for Next Generation AI Infrastructure
Open AI and AMD enter a partnership that will see the AI company deploy up to 6GW of AMD’s Instinct Accelerators to power its next generation infrastructure.
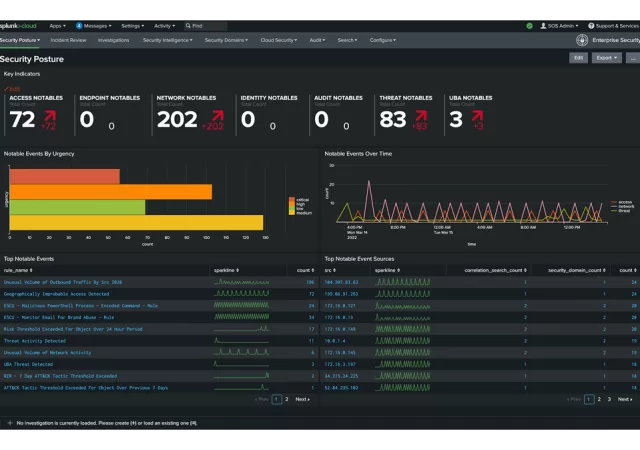
Cisco Introduces Agentic AI-Powered Solutions Powered by Splunk Into Its Security Operations Center
Learn about Cisco’s comprehensive approach to improve threat detection and response through revolutionary AI in the Security Operations Center.
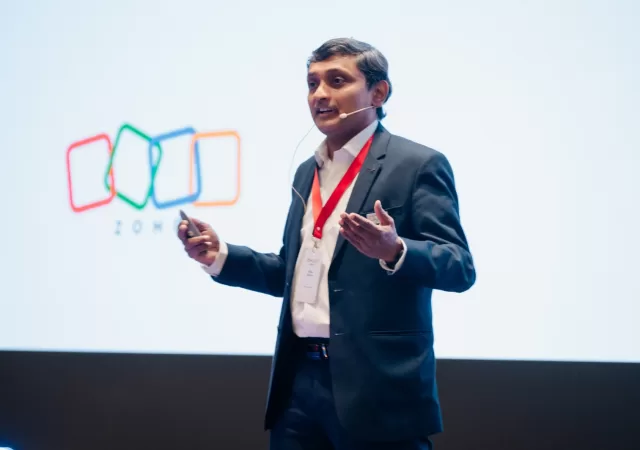
Zoho Introduces Zia and Integrated AI-Tools to Power Productivity
Zoho introduces its in-house LLM, Zia, that powers a new generation of AI-powered enhancements that are being introduced to the Zoho Suite.
Alibaba Cloud Fuels Global AI Race with Strategic International Expansion
Alibaba Cloud announces plans for global expansion going beyond Asia and underscoring the need for compute for AI innovation.
From “Bolt-On” to “Co-Pilot”: Red Hat’s Realistic AI Roadmap for Manufacturing
Digitization and AI deployment in the manufacturing space doesn’t need to revolutionary, it can be evolutionary according to Red Hat’s Kelly Switt.
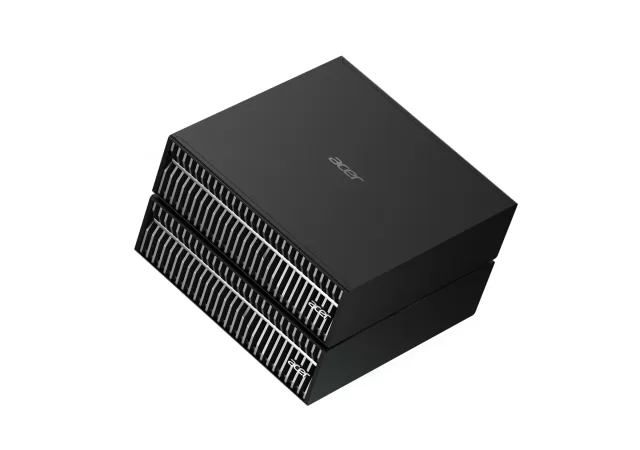
[next@acer] Acer Brings Super Computing To Its New Veriton GN100 with the NVIDIA GB10 Super Chip
Acer’s new Veriton GN100 AI Mini Workstation is packing a huge punch in a minute form factor with NVIDIA’s GB10 Superchip!