Diabetes is one of the leading causes of preventable deaths in Malaysia. In 2020 alone, it accounted for about 2% of the total number of deaths in Malaysia. The disease presents in two forms – Diabetes Mellitus Type I and Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 which are classified according to the age of onset. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus generally presents later in life and is a result of lifestyle choices which lead to over stimulation of pancreatic enzymes leading to glucose tolerance and inefficacy while Type 1 presents in infancy and is usually characterized by the inability of the pancreas to produce insulin.
As the incidence of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 continues to increase in an increasingly obese Malaysia, Malaysian Healthcare professionals (HCPs) are turning to technology to help address the gaps in the diabetic patient management. In a program which is the first of its kind in the country, medical professionals are coming together to spearhead a new approach to managing diabetes.
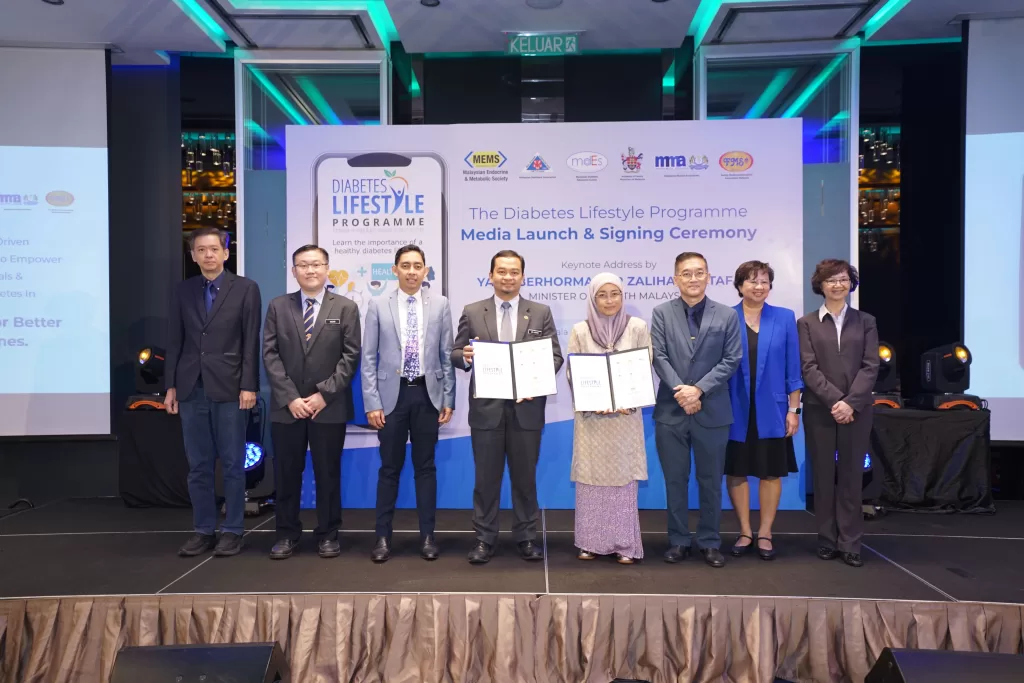

The Diabetes Lifestyle Programme (DLP) sees a collaboration between the Malaysian Endocrine and Metabolic Society (MEMS), the Malaysian Medical Association (MMA), the Malaysian Family Medicine Specialists’ Association (MFMSA), the Malaysian Dietitian’s Association (MDA) and the Malaysian Diabetes Educators Society (MDES) in moving Malaysia’s approach to Diabetes from pharmaceutical intervention to an approach focused more on making effective changes in the patients lifestyle to control the severity of the disease.
Endocrinologist and Chairperson of the Expert Panel spearheading DLP, Datuk Dr Zanariah Hussein, highlights that, “For too long, most healthcare professionals and patients have relied heavily on medications to control high blood sugar levels. Let’s be clear – medications are important when indicated. However, if patients continue leading an unhealthy lifestyle, they may find themselves requiring higher doses or more medications. in contrast, several landmark studies have proven that lifestyle changes can have powerful positive effects, too. Managing one’s diet, getting more active, monitoring blood sugar levels, and losing body weight are basic measures. Lifestyle changes that result in the achievement and maintenance of substantial weight loss will reduce high blood sugar levels, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and even the amount of medications needed. In some cases, diabetes can be reversed entirely!”
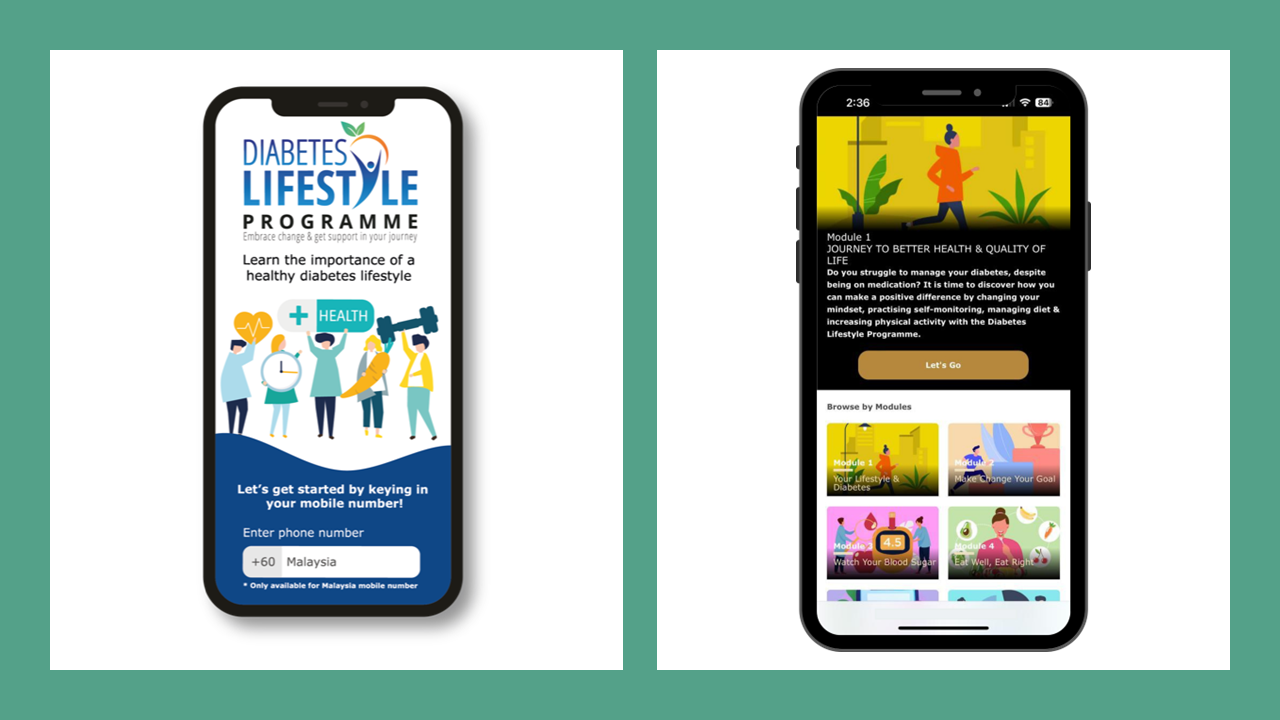
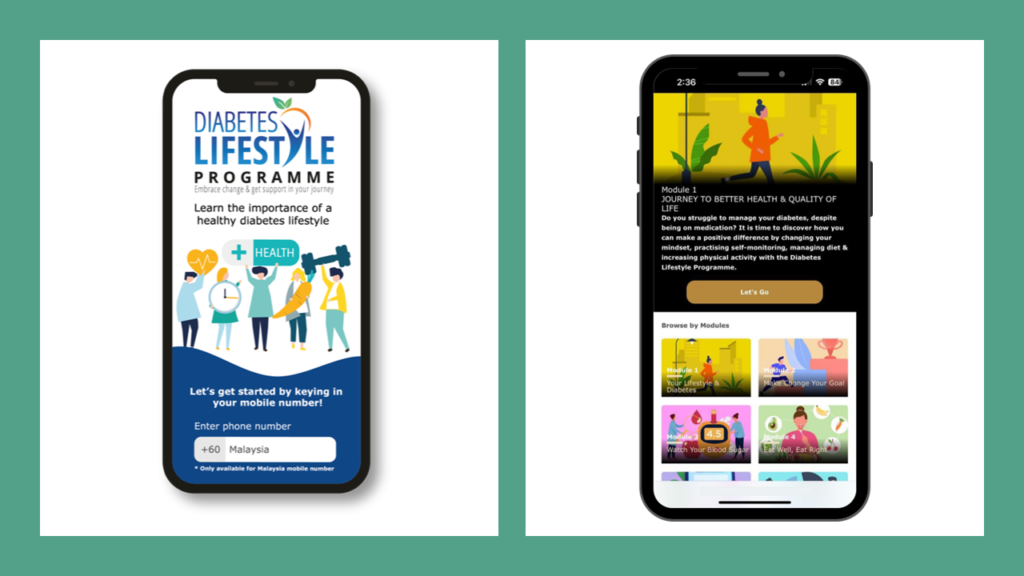
The DLP seeks to empower both healthcare professionals and patients to make these changes through continuous education and through a web app which will be available via the official DLP website. The web app will house educational videos, interactive activities and even a virtual dietitian to help patients understand and make meaningful changes to their lifestyle.
The programme will be entering its first phase with its collaborators signing a memorandum of understanding (MoU). The first phase will see a select number of clinics and healthcare providers being pilots for the program. The DLP secretariat and experts panel hasn’t shared specifics on the eventual national rollout of the program. However, they are encouraging interested healthcare providers to contact the secretariat.
It is hoped that the DLP will be a first step as Malaysia moves towards Diabetes Regression. During the launch, Dr. Osama Hamdy, Medical Director of Obesity Clinical Program at Joslin Diabetes Center and Associate Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School shared research findings which showed how patients who were given the proper support and tools were able to enter Diabetes regression without pharmaceutical intervention. Diabetes Regression is characterized by a HbA1C of less than 5.5mmol/mol.
The DLP web app is looking to be Malaysia’s first step in taking control of its Diabetes endemic. With the proper training and HCP-patient collaboration, it’s not out of reach.